Normally, the chips and the substrate have different thermal expansion coefficients. Therefore, the chips and substrate have different expansion amplitudes after die bond and reflow. For the pads with a size of dozens of microns, these differences in expansion have significant impacts on soldering. It is well known that thermal expansion increases with temperature. Hence, temperature increases will cause an expansion difference between the die-bond chip and the substrate. It is easy to cause misalignment of the pads in the reflow process because of high reflow temperature, leading to a series of reliability deficiencies such as open circuits and cold joint.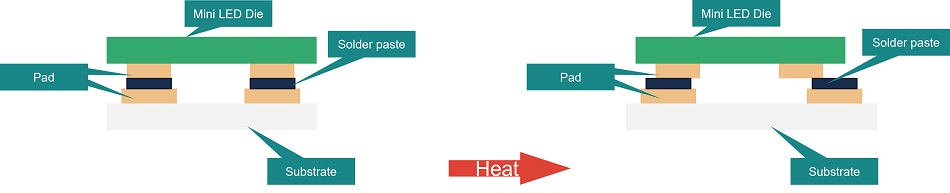
A fundamental solution to reliability deficiency due to thermal expansion coefficient differences is to use low-temperature solder materials which reduce peak reflow temperatures. SnBi/SnBiAg series solder is one of the most common low-temperature solders. The tipical melting point of SnBi/SnBiAg alloy is 139°C, which is nearly 80°C lower than that of SAC305.
Due to limitations of ultra-fine powder manufacturing technology, SAC305 is the main alloy used in ultra-fine die bond solders with the particle sizes of T7 and above. The low-temperature ultra-fine-pitch flip-chip die-bond solder paste developed by Fitech makes up for the blank of low-temperature ultra-fine lead-free solders. The low-temperature solder paste for die bond is made up of SnBiAg powder with the size of T7(2-11μm), T8(2-8μm), or T9(1-5μm) and a special flux, which effectively benefits the low-temperature soldering of ultra-fine-pitch die bond chip.
1. Product: Lead-free solder paste and lead-free epoxy solder adhesive;
2. Flux: No-clean, water-soluble , solvent-soluble; rosin resin, epoxy resin;
3. Applications: Secondary reflow soldering with alloy melting temperatures of 139℃ and low-temperature packaging of Mini LED;
4. Type: T6-T9 (particle size:1-5μm);
5. Advantages: Reducing adverse impacts caused by thermal expansion difference and improving energy saving and environmental protection;
6. Disadvantages: Brittler solder joints than that of SAC products;
7. Processes: Printing, dispensing, needle transfer, and jet printing;
8. Reflow under nitrogen protection (reflow oxygen content ≤100ppm).