Gold Embrittlement in BGA Solder Joints-Shenzhen Fitech
Gold Embrittlement in BGA Solder Joints
Gold embrittlement is a soldering defect that refers to solder joints that contain too much intermetallic compound (IMC), resulting in increased brittleness and reduced reliability. Gold embrittlement mainly occurs in two locations of BGA solder joints, namely between the BGA body and the solder ball and between the solder paste and the immersion plate pads. The BGA solder joint gold embrittlement can be subdivided into two categories, one is the gold embrittlement caused by insufficient heat, and the other is the gold embrittlement caused by excessive gold content.
Insufficient heat in the PCBA soldering process, the metal of the PCB immersion layer will enter the liquid solder, forming AuSn4 build-up in the vicinity of the intermetallic compounds (IMC) of the solder joints, resulting in gold embrittlement of the solder joints. This gold embrittlement problem can be improved by adjusting the PCBA soldering process conditions, such as increasing the soldering temperature and prolonging the soldering time, to ensure that the metal in the solder joint can be fully melted and diffused.
Gold embrittlement caused by excessive gold content
Another type of gold embrittlement problem is caused by the BGA solder joints within the gold content exceeds a certain percentage. When the gold content in the solder joint exceeds 3% wt or even 5% wt or more, the rate of intermetallic compound formation increases, resulting in gold embrittlement of the solder joint. This gold embrittlement cannot be solved by adjusting the reflow soldering temperature profile, but requires other measures. In order to reduce the gold content in the solder joints, you can control the thickness of the gold layer or increase the amount of solder, so that the gold content in the solder joints to maintain the appropriate range.
As far as the PCBA process is concerned, the limited thickness of chemical nickel gold does not lead to excessive gold content within the solder joints, more often than not, the gold layer diffusion is incomplete resulting in gold embrittlement. If the gold layer diffusion is incomplete, even if the thickness of electroless nickel gold is appropriate, there may still be gold embrittlement problems. Therefore, for the PCBA process, to ensure that the diffusion of the gold layer is uniform and complete is also critical.
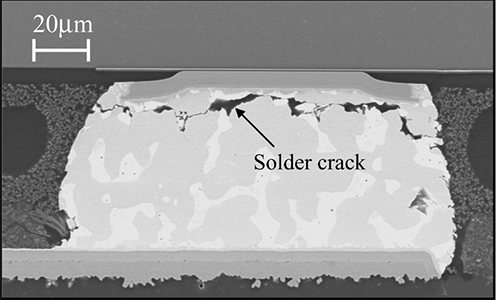
In conclusion, BGA solder joint gold embrittlement is a soldering defect that needs to be taken seriously, and it has a non-negligible impact on the reliability and performance of electronic products. We must recognise that gold embrittlement involves two main aspects: insufficient heat and excessive gold content. Solving these problems requires comprehensive measures, including optimising welding process parameters, controlling the thickness of the gold layer and properly adjusting the welding temperature and time.
In actual production, manufacturers should strictly control the soldering process to ensure that the soldering temperature and time can make the solder joints within the metal fully melted and diffused to avoid the production of gold embrittlement. In addition, for the BGA package design, reasonable setting of the layout and structure of the solder joints to avoid stress concentration on the solder joints, is also the key to reduce gold embrittlement.
At the same time, the scientific and reasonable selection of PCBA materials and processes, control the diffusion of gold layer uniformity and integrity, will be an important direction to solve the problem of gold embrittlement. For the solder joints within the gold content is too high, you can control the thickness of the gold layer and increase the amount of solder, etc., to maintain the gold content in the appropriate range, thereby reducing the risk of gold embrittlement.

















 Back to list
Back to list



