Residue-Free Soldering - The Basic SiP Requirement for Solder Pastes
With Moore's Law of semiconductor chip manufacturing technology reaching its limit, chip packaging gradually develops in the direction of three-dimensional superposition and multi-material anisotropy. The system-in-package technology overcomes the bottleneck of Moore's Law from another perspective. In SiP, solder paste is responsible for the internal component connection, the connection between the integrated components and the components, the connection between the components and the PCB, the connection between the components and FCP, and the connection between the substrate and the outside. Solder paste for soldering and packaging is a paste-like object composed of tin alloy metal powder and flux. After high-temperature reflow, the micro-alloy powder in the solder paste is connected with the copper and nickel metal on the pad to form solder joints. The solder joints have the function of electrical conduction and heat conduction. The organic acids in the flux react and volatilize. However, rosin resin will remain around the solder joint to form the solder joint residue. In general SMT soldering, the residues can stay around the solder joints due to the large size of the components. This kind of solder joint does not need to clean after soldering. However, since the chips are small, the gap between the chips is tiny. The gap between the BGA-connected SiP system and the PCB, POB, and FCP is also small that must be sealed with adhesive. It is required to add underfill like epoxy resin and silicone resin. The underfill and resins in the residue are not compatible. Therefore, the solder paste used in the SiP system integration package should have excellent cleanability. Due to the environmental protection requirement, the prevalent cleaning methods are semi-water-based and water-based cleanings. Water-based cleaning is the priority option.

Figure 1. No-clean lead-free ultra-fine solder paste for SiP developed by Fitech
The rosin residue on the pad can be completely removed by pressure and spray ultrasonic cleaning with the Fitech's W3000-D1 water-based cleaning agent at a cleaning temperature of 60°C. It can meet the manufacturing requirements of solder micro-bumps in mini/microLED and SiP (Figure 2).
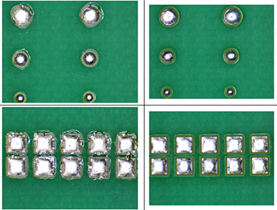
Figure 2. Solder micro-bumps performance











 Back to list
Back to list



