What are the Characteristics of Epoxy Solder Paste/Adhesive?
What are the Characteristics of Epoxy Solder Paste/Adhesive?
With the continuous advancement of lead-free soldering, the mainstream solder pastes used in the packaging market are mostly lead-free types, including tin-silver-copper solder paste, tin-bismuth solder paste, etc. In recent years, many solder pastes have adopted rosin as one of the flux components. This type of flux is popular as it has good activity and wettability. However, the high activity brings the problem of solder residue. If the cleaning is not thorough, it will have a long-term impact on the reliability of solder joints. Therefore, epoxy-based solder paste was developed. Epoxy solder paste and rosin solder paste have the same purpose of surface mounting and forming electrical paths.
Table 1. The application processes of epoxy solder paste and regular solder paste.
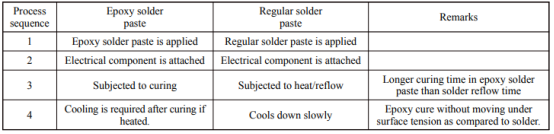
Epoxy solder paste contains alloy solder powder, but epoxy resin is used as the base material of the flux, mixing with organic acids, alcohol solvents, and other components. The flux can be used to remove the oxide layer on the surface of solder powder and pads. Commonly-used epoxy solder pastes/solder adhesives include the tin-silver-copper series, tin-bismuth series, and anisotropic conductive paste. In contrast to rosin flux, epoxy does not require cleaning after soldering. The epoxy resin melts and spreads on the pad during the heating process. When the epoxy resin cools, the viscosity rises rapidly, and a dense adhesion structure is formed to protect the solder joints from the external environment. When the shear force is applied, the thermoset adhesive is first subjected to the external force, which helps relieve the shear force exerted on the solder joints. Therefore, the solder joints can be effectively protected, and the shear strength can be enhanced. Wyung et al. compared the shear strength of solder joints made with conventional eutectic SnBi solder paste and epoxy eutectic SnBi solder paste. They found that the shear strength of epoxy solder paste was almost twice that of regular solder paste.

Figure 1. Shear strength comparison between regular eutectic SnBi solder paste (SB) and epoxy eutectic SnBi solder paste (SB-E) (Wyung et al., 2014).
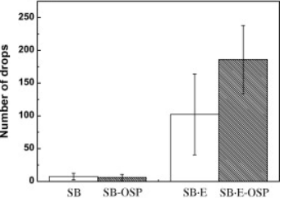
Figrue 2. Drop performance comparison between regular eutectic SnBi solder paste (SB) and epoxy eutectic SnBi solder paste (SB-E) (Wyung et al., 2014).
Since bismuth-containing solder pastes inevitably encounter the brittleness problem, a drop test is required to check the drop performance. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the drop times of the epoxy eutectic SnBi solder paste is significantly higher than that of the regular eutectic SnBi solder paste. Therefore, epoxy flux plays an important role in improving drop resistance.
Anisotropic conductive adhesive is a kind of epoxy solder paste. The epoxy resin can form thermoset adhesive at the solder joints and wrap the solder balls inside to enhance the shear strength and corrosion resistance. Meanwhile, due to the gaps between each solder joint, the package structure is non-conductive in the horizontal direction but excellent conductive in the vertical direction, which is known as anisotropically conductive.

Figure 3. Regular solder paste (left) and epoxy solder paste ((right) application mechanisms.
Fitech is a world-leading provider of microelectronics and semiconductor packaging materials solutions. Fitech’s epoxy solder paste and other products have outstanding wettability, uniform powder particles, and high post-soldering reliability. Welcome to the official website for more information.
Reference
Myung, W.R., Kim, Y. & Jung, S.B. (2014), “Mechanical property of the epoxy-contained Sn–58Bi solder with OSP surface finish”, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, vol.615, pp. 5411-5417.


















 Back to list
Back to list



