What is Reflow Profiles of Solder Pastes

What is Reflow Profiles of Solder Pastes
After the solder paste is placed on the pads, the solder paste needs to be melted by heating and metallurgically react with the pad to form solder joints. The common heating methods include soldering irons, wave soldering and reflow soldering. Wave soldering and reflow soldering are the most popular in the packaging industry because soldering irons are inefficient and not suitable for mass production. This article mainly introduces the reflow process.

Figure 1. Reflow oven appearance.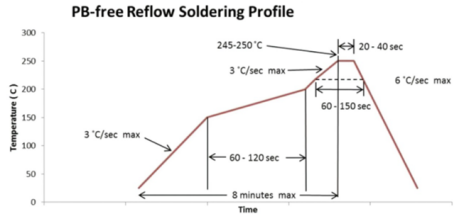
Figure 2. A reflow profile profile for lead-free solder paste (only for reference).
The reflow profile can be divided into four zones, including preheating zone, soak zone, reflow zone, and cooling zone. After the solder paste is deposited on the pads by printing, dispensing, or other processes and the components are mounted, the PCB needs to be preheated. If SAC305 lead-free solder paste is used for packaging, the PCB needs to be preheated in a reflow oven for approximately 100s to about 150°C. The main components of flux in solder paste include rosin, active agent, thixotropic agent, and other solvents. Preheating can volatilize the lower melting point solvent in the solder paste, but the heating rate needs to be controlled. A excessively high heating rate will increase the thermal stress of the package, which will easily lead to thermal creep, cracks, and other reliability problems of the solder joints.
The soak zone allows the solder paste to fully wet the pad. The flux can effectively improve the wettability of the solder paste, remove the oxide layer on the pad, and change the surface tension of the melting solder. In addition, soak zone allows further evaporation of the solvent components in the flux, thereby minimizing solder residues.
After the solder paste reaches the reflow zone, the temperature rises rapidly to reach the peak reflow temperature. Generally, the peak reflow temperature is 25-45°C higher than the solder paste melting point. The solder paste will completely melt and wet the pads. The flux activity is at its strongest at this stage. Under high temperature, intermetallic compounds (IMCs) generate due to interfacial reactions. If SAC305 lead-free solder paste is used, Cu6Sn5 will be generated. A small amount of Cu6Sn5 is beneficial for the connection between the solder paste and the pad. It should be noted that excessive reflow time should be avoided as it can cause massive growth of the IMCs , which increases the brittleness of the solder joints. Generally, the holding time above the melting temperature is about 30s, which needs to be adjusted according to the reflow parameters.
Lastly is the cooling zone. Cooling solidifies the solder paste into a solder joint and can refine the grain structure of the solder joint and enhance the mechanical strength. Reasonable control of cooling rate and time has a great impact on solder joint reliability. If the cooling rate is too slow, the solder paste may oxidize without nitrogen protection and warp due to thermal expansion mismatch, resulting in poor solder quality. However, if there is a fast cooling, the thermal stress of the solder joints increases, resulting in cracks. The common cooling speed and time are 4°C/s and 100s, respectively, which need to be adjusted according to the real situation.
Fitech is committed to the development and production of packaging solder paste. Fitech’s lead-free products cover tin-silver-copper and tin-bismuth alloy combinations, which can be used in a variety of packaging scenarios and can produce reliable solder joints. Welcome to consult.

















 Back to list
Back to list



