Effect of Cu Content in SnAgCu Solder on Warpage_Fitech Solder Paste
Effect of Cu Content in SnAgCu Solder on Warpage
Warpage is the phenomenon of bending or warpage of materials or components during the manufacturing or soldering process, usually in the fabrication and assembly of electronic components. This buckling usually occurs in board or film-like materials such as printed circuit boards (PCBs), chips, electronic packages, plastic parts, etc. Warpage can cause a component to fail to meet specifications and, in extreme cases, can even damage the component or cause performance problems in electronic equipment.
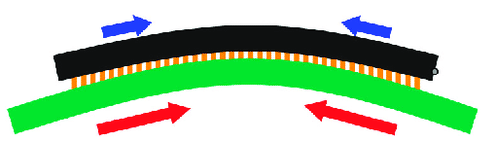
Figure 1. Warpage due to mismatched coefficients of thermal expansion
The solid-liquid co-existence zone is the region of the solder where both solid and liquid phases are present in the solder during solidification. The width of this zone is influenced by the composition and temperature of the solder. In general, the wider the solid-liquid co-existence zone, the greater the likelihood of warpage, as this means that the solder takes longer to solidify, resulting in greater thermal and internal stresses.
The effect of the solid-liquid coexistence zone width on the occurrence of warpage cannot be ignored. Especially when SnAgCu or SnCu solder alloys are used for wave soldering, the Cu content in the solder bath will change. That is, the PCB wiring and pads on the Cu will be dissolved into the solder bath, the use of a long time, the concentration of solder Cu in the solder bath is increasing, solid and liquid coexistence zone width will change.
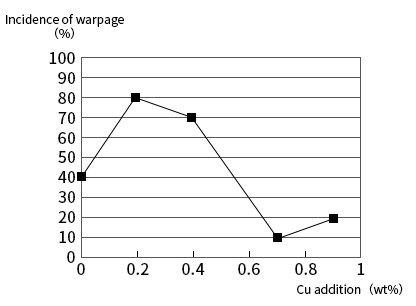
Figure 2. Effect of change in Cu content on the incidence of warpage when using SnAg3.5CuX alloy.
In the figure, the degree of warpage occurrence when soldering components with SnPb-plated pins using SnAg eutectic compositions, the incidence of warpage reaches a maximum when the Cu content is increased to 0.2 wt%. Then with the increase of Cu content, the incidence of warpage decreases slowly, when the Cu content increases to 0.75wt% when the incidence of warpage reaches a minimum, and then slowly increase. Obviously, the eutectic component can minimise the incidence of warpage. Therefore, effective management of the solder composition in the solder bath, including Pb mixed in from the pin plating and Cu dissolved from the substrate, is critical to ensuring the success of the soldering process.
In order to reduce or avoid the occurrence of warpage, the Cu content in the solder bath needs to be controlled within a suitable range, typically between 0.5% and 1.0%. In addition to this, some of the following methods can be used:
Optimise the soldering temperature and time so that the printed board or components are heated evenly and adequately.
Optimise the welding parameters, so that the printed board or component force balance and appropriate.
Optimise the design, processing, cleaning and storage of the printed board or component to improve the quality and stability of the printed board or component.
Use appropriate gate position and form to avoid localised overheating or overcooling.
Use auxiliary fixtures or supports to fix the printed board or components to prevent deformation.
The solder paste products produced by Fitech cover a variety of alloys, particle size T2 ~ T10, to meet the needs of different scenarios of encapsulation, welcome to call us for more information.

















 Back to list
Back to list



