Characteristics of No-Clean Solder Paste (1): Analysis of Corrosive Mechanism of Residues
Characteristics of No-Clean Solder Paste (1): Analysis of Corrosive Mechanism of Residues
In order to meet the increasing requirements of ordinary users for the use of electronic devices, the number of chips inside the components has become higher, and the chip size has become smaller. However, it is difficult to clean small electronic packages, resulting in the development of no-clean solder pastes. The flux component of the no-clean solder paste contains weak organic acids, such as carboxylic acids, which can remove the oxide layers from the pads, leaving only a small amount of acid ion residues. Although there is the little residue after soldering, it can not be ignored for some high-precision devices. Therefore, the corrosivity analysis of the no-clean solder residue is still a popular topic.
1. Why is the residue corrosive?
Carboxylic acid is mostly used in the market as a component of flux activator. Carboxylic acid is a weak organic acid that will react with copper oxide. Organic acids typically have polar functional groups, which are easy to combine with water in the environment and generate acidic solutions, which will have a corrosive effect on PCBs.
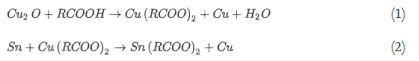
Eq. (1)&(2): Reaction equations of carboxylic acid and copper oxide.
In addition to carboxylic acid, rosin resin is added to rosin-based no-clean solder paste to prevent reoxidation of the soldering surface. However, the resin will not volatilize after soldering. Thus, more solid acid phosphate will be left as an ionic residue. In order to avoid producing solid residues, some manufacturers use resin-free solder paste. If the carboxylic acid partially react with the metal oxides, the unreacted carboxylic acid will be dehydrated at high temperatures and form an anhydride, resulting in the formation of carboxylic acid and water. Since acid anhydride has strong hygroscopicity, it is easy to form a thick conductive layer, which increases the possibility of PCB leakage current.
2. Factors affecting corrosion of weak organic acids
2.1 Solubility
The higher the solubility of organic acids, the easier it is to interact with water and generate more ionic residues. The low solubility of weak organic acids can be reached when they contain a high molecular weight, less polar functional groups, and an even number of carbon atoms. Consequently, the residue of no clean solder paste adopting a weak organic acid is minimized (Wakeel et al., 2021).
2.2 Relative humidity of deliquescence/efflorescence
The relative humidity of deliquescence and efflorescence significantly affects the water absorption capacity of organic acids (Wakeel et al., 2021). For lower relative deliquescence and efflorescence humidity, organic acids, such as carboxylates, will absorb water earlier and form a conductive layer, thus increasing the conductivity of PCBA. For example, the relative deliquescence and efflorescence humidity of DL malic acid are lower than that of succinic acid. It was found that DL malic acid absorbed water earlier (Piotrowska et al., 2018). At the same time, the low relative efflorescence humidity makes the carboxylate transform into a solid faster, which will increase the leakage current of PCBA.
2.3 Number of functional groups and molecular chain length
The increase of functional groups of weak organic acids will promote the interaction with water molecules, thus enhancing the moisture absorption of organic acids. In addition, the distance between functional groups also determines the polarity of acids. The smaller the distance between functional groups, the easier the water stays and the stronger the moisture absorption capacity. Therefore, the residue is more acidic. Piotrowska et al. observed that compared with linoleic acid, adipic acid, succinic acid, and glutaric acid, the no-clean solder paste with the formula of palmitic acid is the least corrosive because palmitic acid has the least number of carboxyl groups and the longest chain.
Fitech can produce high-quality no-clean solder pastes regarding customer needs. The no-clean solder paste products generate less residue after soldering and can produce solder joints with high reliability. Welcome to the official website for more information.
Reference
Piotrowska, K., Din, R.U., Grumsen, F.B., Jellesen, M.S. & Ambat R. (2018). “Parametric study of solder flux hygroscopicity: impact of weak organic acids on water layer formation and corrosion of electronics”, J. Electron. Mater., vol.47 (7), pp. 4190-4207.
Wakeel, S., Haseeb, A.S.M.A., Afifi, M.A., Bingol, S. & Hoon, K.L. (2021). “Constituents and performance of no-clean flux for electronic solder”. Microelectronics Reliability, vol.123.


















 Back to list
Back to list



