Introduction to Solder Paste High-Temperature Reliability Test - Shenzhen Fitech

Introduction to Solder Paste High-Temperature Reliability Test - Shenzhen Fitech
It is inevitable that electronic products will generate heat when they are used, which makes the internal of products vulnerable to thermal stress. The thermal expansion coefficient between the solder joints and PCB substrate is different, and reliability problems are easy to occur after receiving thermal stress. Therefore, it is usually necessary to conduct a high-temperature reliability test on solder joints after soldering.
1. Damp heat test
The damp heat test can also be called the 85/85 test. 85/85 means that the test ambient temperature and humidity are 85℃ and 85%RH, respectively. According to the specific test requirements, sometimes the test humidity will be set to 95% RH and the temperature will be set between 45℃ and 85℃. The test time is generally 1000 hours. The damp heat test can be carried out in a temperature humidity chamber.
Test purpose: The damp heat test is used to verify whether the process materials (solder paste, etc.) that directly or indirectly participate in the product composition during the production of electronic products will have an impact on the reliability of products under a certain temperature and humidity. The damp heat test is a verification tool frequently used in PCBA.
Scope of application:
lTo verify the corrosivity of residues of solder paste used in PCBA generation;
lCorrosion verification of wave soldering flux residues;
lVerification of compatibility of various adhesives used by PCBA with PCB and components;
lTo cooperate with the electromigration test.
2. Thermal cycling test
The thermal cycling test is to put the test components in a chamber where temperature varies from around -45℃ to around 100℃ or vice versa for a certain period of time. Some automotive components may require higher upper-limit temperatures. According to the JESD22-A-104 standard, the minimum soak time of the element level test is 1 minute, while the solder paste bonding test normally adopts 5 minutes, 10 minutes, and 15 minutes. The heating and cooling rate of the thermal cycling experiment is generally controlled at 10-15℃/min. For the test of solder joints, the temperature change rate is 15℃/min. Extreme high and low temperatures can simulate the real working environment, such as high temperatures in the day and low temperatures at night, which help manufacturers ensure the reliability of solder joints.
Test purpose: The thermal cycle test can be divided into charged tests and non-charged tests. The non-charged thermal cycling test focuses on determining the thermal aging impacts of solder joints and devices on performance reliability. The purpose of charged thermal cycling test is to measure the stability of devices at different temperatures.
Table 1. Product classification and operating conditions.
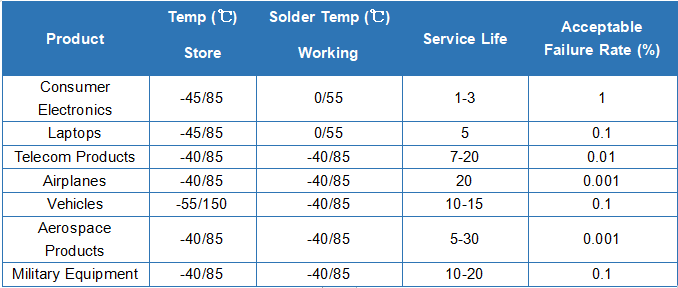
Table 2. Common temperature cycling test conditions.
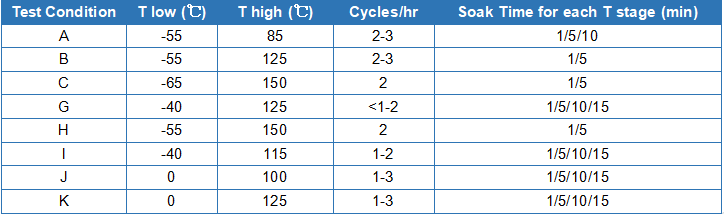
One of the reasons for solder joint fracture during temperature cycling is the growth of intermetallic compounds in the solder joints. The growth of intermetallic compounds caused by temperature changes leads to coarse grains and reduced solder joint strength.
Shenzhen Fitech’s lead-free ultrafine solder paste products have been strictly verified, and the solder joints can maintain high mechanical strength and conductivity throughout the damp heat test. Besides, Fitech’s ultrafine solder pastes can maintain high reliability during temperature cycling. Welcome to contact us for more product information.

















 Back to list
Back to list



