Effect of ENIG Au Layer Thickness on SAC305 Soldering - Shenzhen Fitech

Effect of ENIG Au Layer Thickness on SAC305 Soldering - Shenzhen Fitech
To protect PCB pads from oxidation, surface finishes are often required. ENIG is an efficient surface finish method. It can significantly resist oxidation by successively plating the Ni layer and Au layer on the bonding pads. The consensus of the industry on the nickel layer is that nickel can effectively reduce the diffusion rates of Sn and Cu atoms, thus reducing the thickness of intermetallic compounds (IMCs). Many people believe that the Au layer will affect the wettability of solder on the pad, but there are few relevant studies.
To deeply understand the influence of the ENIG Au layer thickness on the solder wettability, Wang et al. used SAC305 solder paste to conduct a reflow soldering test on ENIG-Cu pads and analyzed the influence of the Au layer thickness on the soldering effect. The thickness of the Ni layer on the test pads was 5μm. The thicknesses of the Au layer were 30nm, 50nm, and 80nm.
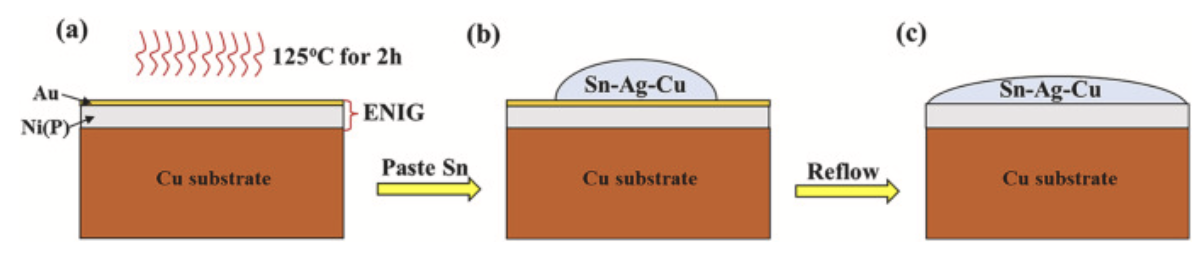
Figure 1. SAC305 soldering process.
Test result
Through XPS detection, it was found that Ni and Ni oxides appeared on the surface of the Au layer during heat treatment at 125℃. In theory, there will be no Ni on the surface of the Au layer of ENIG, but Wang et al. found in the experiment that the content of Ni increased on the surface of the Au layer after heat treatment. In addition, Ni oxide on the surface of the Au layer was mainly Ni (OH) 2 and NiO. It is noteworthy that the content of Ni (OH) 2 and NiO decreased with the increase of Au layer thickness. When the thickness of the Au layer was 30nm, the Ni content was about 6.7%. As the thickness of the Au layer increased to 80nm, the Ni content decreased to 4%.

Figure 2. XPS spectrum of Au layer surface (a) Ni 2p spectrum (b) O 1s spectrum.
Mechanism of Ni accumulation on the surface of the Au layer
For ENIG, the Au layer not only protects the pad from oxidation but also protects the Ni layer from oxidation. However, due to the difference in atomic radii (RNi=1.25Å and RAu=1.44Å), Ni atoms have the opportunity to diffuse to the surface of the Au layer along the atomic gap when heated. Once the heat treatment is exposed to the air, Ni diffused to the surface of Au will be oxidized to Ni (OH) 2 and NiO.
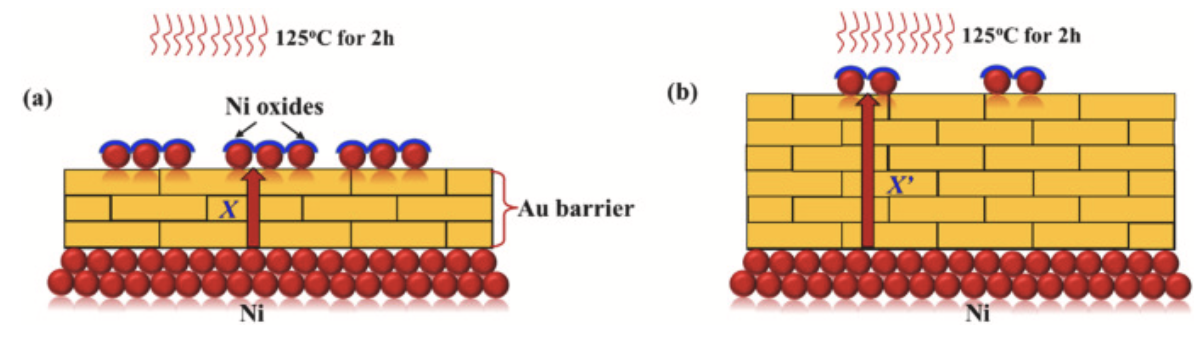
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of Ni diffusion and oxidation.
Effect of Au layer on wettability
When the thickness of the Au layer increases, the solder can spread more smoothly on the pad, which means that the solder has better wettability on the pads. The reason is that the increase in the thickness of the Au layer can reduce the formation of nickel oxide, ensuring the excellent wettability of the solder paste.
Shenzhen Fitech can produce ultra-fine solder paste products (≥T6) with excellent wettability, which can be applied to PCBs with various surface finishes. Moreover, Fitech’s solder paste has narrow particle size distribution, excellent collapse resistance, and outstanding post-soldering mechanical strength. Welcome customers to cooperate with us.


Reference
Wang, J., Sun, Q., Tang, X.X. & Akira, K. (2022). Influence mechanism of Au layer thickness on wettability of Sn–Ag–Cu solder on heated ENIG pads. Vacuum, vol.201.

















 Back to list
Back to list



