Addition of Silver Nanoparticles Improves Wettability of SnAgCu Solder Pastes_Shenzhen Fitech
Addition of Silver Nanoparticles Improves Wettability of SnAgCu Solder Pastes
Due to the requirements of EU regulations (ROHS), lead-free solder pastes have been commonly used for printed circuit board (PCB) assembly in SMT. One of the most commonly used is the SnAgCu alloy series solder paste. It is well known that the addition of nanoparticles can change certain properties of materials.Koscielski et al. attempted to change the wettability of lead-free solder paste with silver nanoparticles. By adding different particle sizes of silver nanoparticles to SAC solder paste, the spreading effect of the solder paste and the difference in the microstructure of the solder joints were observed.
In their study, Koscielski et al. used silver nanoparticles of varying sizes (138 nm-Ag3 and 21 nm-Ag4 to 9.6 nm-Ag5.5). Six test samples for spreading measurements were obtained by adding different amounts of silver nanoparticles to the base SAC305 solder paste: 1% and 4% by weight, as well as three different types of silver particles (9.6 to 138 nm). A 0.2 mm thick copper plate (50 mm x 50 mm) was used as the measurement substrate. A 500 mg sample of solder paste was placed in the central part of the copper substrate and then reflowed for 30 seconds at temperatures of 220, 230, 240, and 250°C.
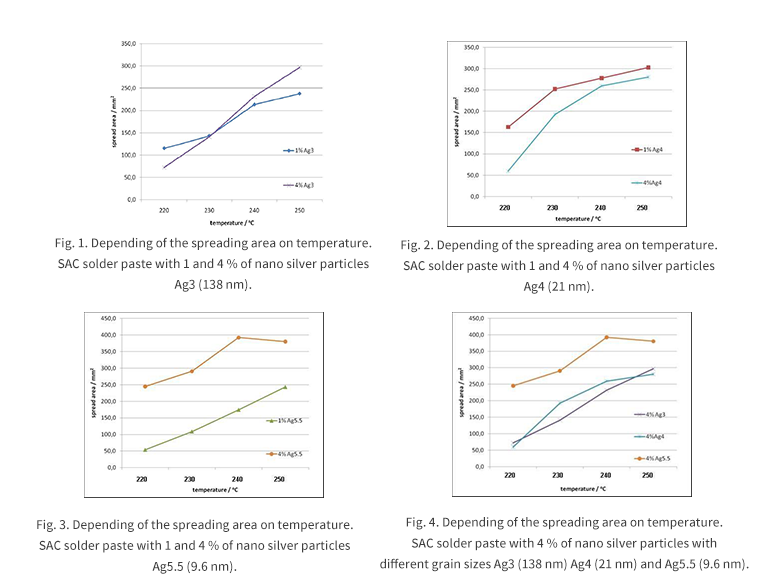
It can be seen that reducing the particle size of the doped silver nanoparticles from 138 nm to 9.6 nm improves the wetting properties of the SAC solder paste. Figures 1, 2 and 3 show that the spreading area on the copper substrate increases in the temperature range of 220-250°C. The difference at 220°C was especially pronounced for all samples when more silver nanoparticles were added. As shown, the greatest effect on spreading was seen when 4% of silver nanoparticles were added. The largest change in spreading is observed when the smallest particles with a size of 9.6 nm are used.Figure 4 shows the effect of the amount of different particle sizes on the spreading effect when 4% of silver nanoparticles are added. The smaller the nanoparticles, the better the spreading effect. The difference is noticeable when particles of 9.6 nm size are used.
Koscielski et al. also found that silver-doped nanoparticles change the microstructure of solder joints. At 4%, the addition of smaller particles produced Ag3Sn structures that grew inside the solder joint (Figures 5 and 6). The smaller the particles used, the larger the star-like structure.

The addition of silver nanoparticles positively affects the thickness of the IMC layer. In all cases (1% or 4% addition), the thickness of the IMC was comparable or smaller than the reference sample with a thickness of 2.7 µm. The measured data are presented in Tables 1 and 2. EDS analysis showed that the IMC composition of the solder joints was Cu6Sn5.
Table 1. IMC thickness at 1% silver nanoparticle addition measured by scanning electron microscopy.
Thickness/μm | Ag3(1%) | Ag4(1%) | Ag5.5(1%) |
Minimum | 0.91 | 1.83 | 0.59 |
Maximum | 3.46 | 4.98 | 3.60 |
Average | 2.12 | 3.20 | 2.26 |
Table 2. IMC thickness measured by scanning electron microscope for silver nanoparticle addition of 4%.
Thickness/μm | Ag3(4%) | Ag4(4%) | Ag5.5(4%) |
Minimum | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.58 |
Maximum | 3.51 | 1.63 | 3.53 |
Average | 1.89 | 1.15 | 2.30 |
The structure of IMC is rod shaped with the addition of 1% nanosilver and scallop shaped with the addition of 4% nanosilver. (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
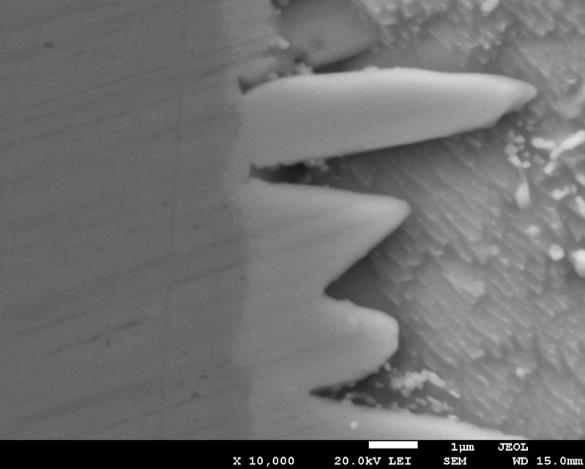
Fig. 7. Example of microstructure of IMC of solder joints containing 1% about 21 nm of silver nanoparticles (Ag4).
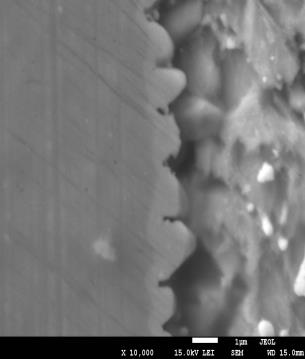
Fig. 8. Example of microstructure of IMC of solder joints containing 4% of silver nanoparticles (Ag4) of about 21 nm.
The addition of silver nanoparticles can significantly enhance the performance of SAC 305 solder paste, including spreading ability and solder joint microstructure. The smaller the added particles, the larger the spreading area. In addition, nanoparticle addition had a favorable effect on the thickness of the intermetallic compound layer, which on average was measured to be predominantly lower than the reference sample.
Shenzhen Fitech has been committed to lead-free solder paste research and development and production for many years, the solder paste products produced are highly reliable, good wettability, and suitable for different viscosity, alloy and particle size requirements. If you want to know more about our solder paste products and services, welcome to call us, we will be happy to serve you.
Koscielski, M., Bukat, K., Jakubowska, M., & Mlozniak, A. (2010). Application of silver nanoparticles to improve wettability of SnAgCu solder paste. 33rd International Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology, ISSE 2010. doi:10.1109/isse.2010.5547345.

















 Back to list
Back to list



