The effects of SAC305-SiC composite solder on intermetallic compounds_Shenzhen Fitech
The effects of SAC305-SiC composite solder on intermetallic compounds_Shenzhen Fitech
SAC305 is a common medium-high-temperature solder commonly used in secondary reflow soldering. SAC305 has high conductivity and soldering strength, which can meet the usage requirements of most microelectronic products. The main factor affecting the soldering strength of SAC305 is the growth of intermetallic compounds (IMCs). IMCs nucleate and grow due to interface reactions during soldering and aging, and their brittleness may reduce the strength of the solder joints. SiC is a ceramic material with unique chemical stability and ultra-high melting point and possesses excellent electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. Many studies have shown that SiC particles can be refined β- Sn and IMCs play a role in enhancing solder joints.
SAC305-SiC solder
Pal et al. chose to combine a small amount of SiC (1-3μm) And SAC305 (20-24μm) The alloy powder is mixed, and reinforced solder is prepared by planetary ball milling process. The solder is prepared by stirring at room temperature at the speed of 200rpm for 1 hour. The sample is placed on a copper substrate for reflow soldering and then cooled in air. SAC305 xSiC/Cu (x=0, 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5wt%) solder samples were heated in a furnace at 533K for 30 minutes and subsequently subjected to aging testing. By observing the growth of IMC, the effect of SiC on solder joints can be understood.
What are the impacts of SiC on IMCs?
l Figure 1 shows the effect of different SiC addition amounts on the IMCs layer. It can be observed that the IMC layer of ordinary SAC305 solder is thicker. The thickness of the IMCs layer in SAC305-SiC continuously decreases until the addition of SiC particles reaches 1.0 wt.%. For SAC305-1.0wt.%SiC composite solder, the thickness of the Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn was decreased by 43.8% and 39.6%, respectively. As SiC further increases, IMCs will increase slightly.
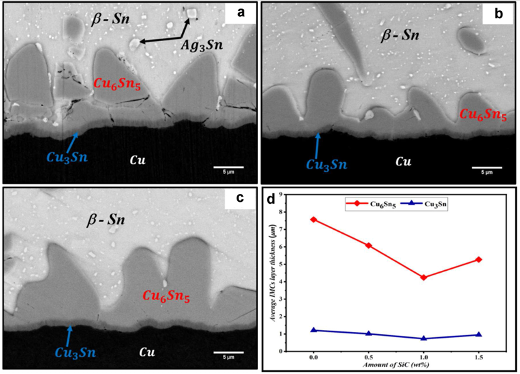
Figure 1. IMC of SAC305 SiC solder after 100h of aging at 413K. (a) SiC=0; (b) SiC=1wt%; (c) SiC=1.5wt%.
l Copper atoms diffuse through various channels and form η-Cu6Sn5 grains. η- Cu6Sn5 grains deposit on larger IMCs because smaller particles have higher solubility. As the reflow time increases, Cu6Sn5 is controlled by grain coarsening, ultimately blocking the channels between grains. SiC particles do not melt due to their high melting point but are absorbed in the solder joint body and can act as barriers to the diffusion of copper atoms.
l The solder sample (SAC305-1.0wt.% SiC/Cu) was reflowed at 533K for 30 minutes and aged at 413K, 423K, 433K, and 443 K (25, 50, 75, and 100h). From Figure 2, it can be observed that the growth of IMC layers accelerates with increasing aging time and temperature. In this study, the thickness of Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn layers showed a linear relationship with the square root of aging time.
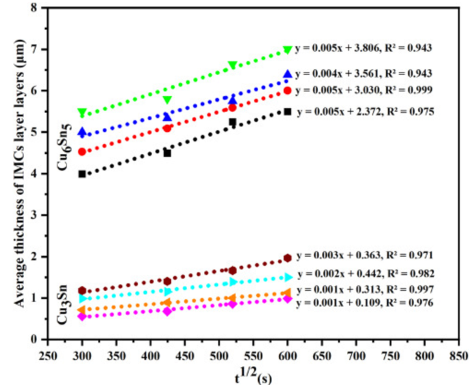
Figure 2. IMC growth rates of SAC305-1.0wt%SiC at different aging temperatures and times (413K, 423K, 433K, and 443K).
Fitech’s solder products
Fitech's solder paste, epoxy solder paste, and T2-T10 solder powder are widely used in various fields of microelectronics and semiconductor packaging. Fitech's products are widely recognized by global SMT electronic chemical manufacturers, micro optoelectronic manufacturers, and semiconductor packaging testers.
Reference
Pal, M.K., Gergely, G. & Gacsi, Z. (2023). Growth kinetics and IMCs layer analysis of SAC305 solder with the reinforcement of SiC during the isothermal aging condition. Journal of Materials Research and Technology.

















 Back to list
Back to list



