Solder Paste Selection for Laser Chip Placement and Packaging - Tin-Base, Indium-Base, and Gold-Base Solders
Solder Paste Selection for Laser Chip Placement and Packaging - Tin-Base, Indium-Base, and Gold-Base Solders
The semiconductor laser is one of the most widely-used optoelectronic devices. With the continuous advancement of technology and the improvement of device mass production capabilities, semiconductor lasers have more applications in other fields. A semiconductor laser adopts a semiconductor as laser material. The laser varies with different material structures. The characteristics of semiconductor lasers are small size and long life. In addition to communication, semiconductor lasers can also be used in radar, sound measurement, and medical treatment.

High-power lasers generate massive heat per unit area due to the large output power of a single chip. If the heat dissipation technology is not proper, it is easy to cause chip failure and rapid performance degradation.
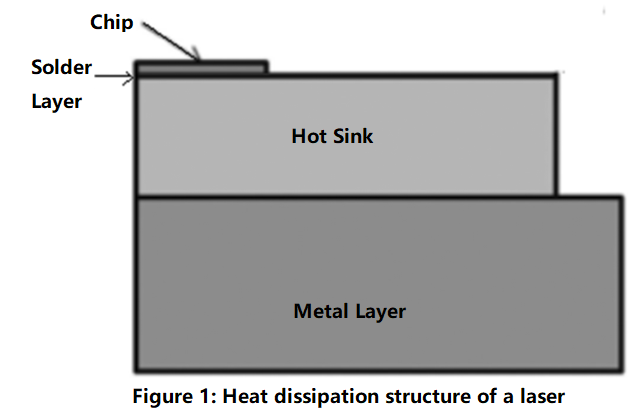
The heat dissipation components of the semiconductor lasers are mainly composed of laser chips, soldering layers, heat sinks, metal layers, etc. The soldering layer connects the chips and heat sinks together by soldering. In order to reduce thermal resistance when high-power semiconductor lasers are used, some materials with relatively high thermal conductivity are often adpoted in soldering, such as the gold-tin solder. There will be many components in the entire packaging process, including chips, soldering layers, heat sinks, and metal layers. The heat sinks and the metal layers are applied to transfer the heat of the laser chips. The semiconductor laser will eventually form an excellent heat dissipation ability that can extend the laser operating life.

SAC Solder Paste SnBiAg Solder Paste SnBiAgSb Solder Paste SnBiAgX Solder Paste SnBi Solder Paste BiX Solder Paste AuSn Solder Paste SnSb Solder Paste SnPb Solder Paste Anositroic Conductive Paste Flux for Ultra-FIne-Pitch Packaging

As a part of the laser chip heat dissipation system, the selection of solder pastes is important. Which tin-based solder, indium-based solder, and gold-based solder is the most suitable for laser chip packaging?
Tin-based alloys are mainly composed of tin, including tin-lead and tin-silver-copper alloys. Due to poor metal fatigue properties, tin-based alloys are limited in micro-device solderings such as MEMS and lasers.
The chip soldering of the lasers usually adopts gold-tin alloys, and indium-based solders were also used earlier.
In micro-assembly, the solder layers cannot be thick. Metal fatigue needs to be considered. The thermal fatigue characteristics of tin-based solder make it unsuitable for thin-layer materials.
Indium-based and gold-based solders have outstanding fatigue resistance to achieve high-strength solderability.
Due to electromigration and thermal migration of indium-based materials, long-term laser operation will generate voids in the solder joints, resulting in reliability issues.
Gold-based materials do not present the migration phenomenon, so they have sufficient strength and long-term reliability.
Gold-based solders have higher thermal conductivity than gold-silicon alloys/gold-germanium alloys, which are more suitable for laser chip mounting.
The FH-280 series eutectic gold-tin solder paste produced by Fitech consists of 80%wt Au and 20%wt Sn. The excellent characteristics of FH-280 solder and Fitech 's advanced powder manufacturing technology are the secrets to producing FH-280 solder with several attractive features such as high tensile strength, excellent corrosion resistance, outstanding thermal creep, highly compatible with precious metals, superior electrical conductivity, extraordinary thermal conductivity, etc. FH-280 series solder paste has a melting point of 280℃. The particle sizes can reach the categories of T3-T6, which support printing and dispensing processes.
Gold-tin solder must be applied accurately to achieve good results. The factors affecting the soldering quality are gold-tin solder compositions, soldering parts, solder surface quality (such as oxide, pollution, flatness, etc.), and process factors (furnace temperature profiles, maximum temperatures, gas compositions, tools, etc.). The melting points of gold-tin alloys are sensitive to the metal compositions. When the mass ratios of gold are higher than 80%, the melting points increase sharply. Soldering parts usually have gold layers. The gold layers will immerse in the solder when reflow soldering. A thick gold layer, a thin pre-forming solder, and a long soldering time will cause excessive gold immersed in the solder, which increases the melting point. Therefore, the various soldering parameters need to be optimized. The conventional peak temperature of the furnace should be about 350 ℃. The soldering time is 2 to 4 minutes, and the yield can reach above 98%.
Conclusion
Because of the moderate melting point (280℃), the gold-tin eutectic alloy has a series of advantages such as high strength, no flux, good thermal conductivity, excellent permeability, low viscosity, easy soldering, high corrosion resistance, outstanding creep resistance, etc. It is widely used in ceramic packaging caps, chip bonding, ceramic insulator soldering, and the soldering of high-power semiconductor laser chips.


















 Back to list
Back to list



