Ultra-Fine-Pitch LED Display Chip Structure and Selection of Lead-Free Solder Paste for Flip-Chip LEDs
Ultra-Fine-Pitch LED Display Chip Structure and Selection of Lead-Free Solder Paste for Flip-Chip LEDs

Wire-bonding LED chips, vertical LED chips, and flip-chip LEDs are three different structures of LED chips. Different structures of LED chips influence the selection of lead-free solder pastes.
1. LED Chip Definition
The LED chip is a semiconductor device that realizes the photoelectric conversion function. It is made by processing semiconductor chips on epitaxial wafers. This semiconductor chip fabrication process is to transfer metallic organic compounds to a homogeneous or heterogeneous substrate at a suitable temperature and to grow semiconductor thin film materials with specific photoelectric properties through chemical reactions.
2. LED Chip Lighting Principle
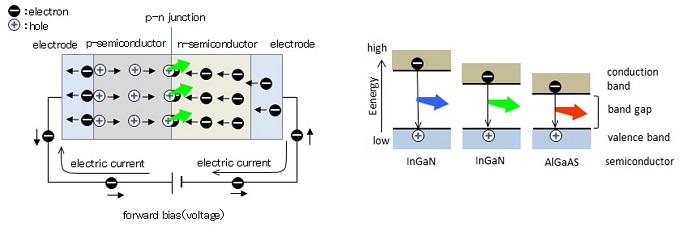
Each pixel of the LED display screen is composed of a set of RGB (red, green, and blue) chips, which belongs to the self-luminous display technology. RGB LED luminescent materials are different according to the various sizes of the band gaps between the conduction bands and the valence bands of the materials. Thus, the energy released is different when the materials are excited, which is reflected by the different wavelengths of electromagnetic waves. The human eye receives different light colors of electromagnetic waves with different wavelengths. The core part of the LED is the p-n junction.
3. LED Chip Structure
There are three main types of LED chip structures: wire-bonding LED chips, vertical LED chips, and LED flip-chips.
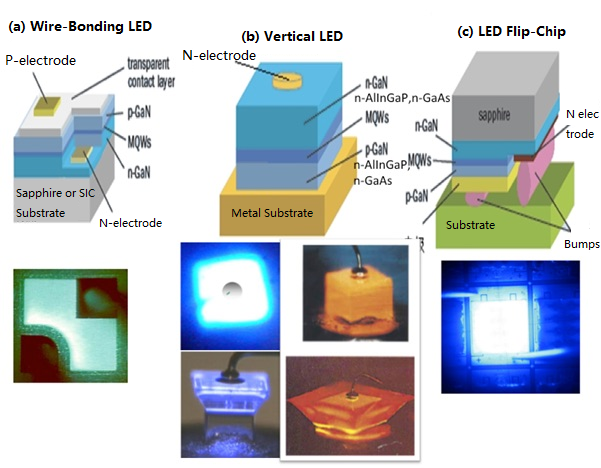
The wire-bonding LED chip electrodes are above the light-emitting surface. The components from top to bottom are P-GaN, light-emitting layer (PN junction), N-GaN, and substrate. The vertical chip structure adopts Si, Ge, Cu, and other materials to replace the sapphire substrate, improving heat dissipation efficiency. The vertical LED electrodes are on both sides of the LED epitaxial layer to avoid local current congestion and high temperature. Flip-chip structure consists of N-GaN, light-emitting layer (PN junction), P - GaN, metal electrodes, and bumps.
The wire-bonding structure mainly uses blue-green LED chips. The vertical structure applies red LED chips. The flip chip is suitable for red, blue, and green LED chips.
For the previous fine-pitch LED (1.0mm≤Pitch≤2.5mm) packaging, wire-bonding blue-green LED chips, and vertical red LED chips are used. With the rise of mini-LED and micro-LED and the shrinking of chip size and pixel pitch, the wire-bonding structure is limited by space due to the need for bonding wires when the pixel pitch is less than P0.78 (data from experts). Therefore, it is required to adopt a LED flip-chip structure.

SAC Solder Paste SnBiAg Solder Paste SnBiAgSb Solder Paste SnBiAgX Solder Paste SnBiSolder Paste BiX Solder Paste AuSn Solder Paste SnSbSolder Paste SnPbSolder Paste Anisotropic Conductive Paste Flux for Ultra-Fine-Pitch Soldering

4. Lead-Free Solder Paste for Flip-Chip LED
The majority of ultra-fine-pitch displays adopt the method of mini-LED flip-chip. The main advantages of flip-chip include:
The mainadvantages of flip-chip in display application | |
1 | No need for gold wires, dense arrangement, smaller pixel pitch, and simplified |
2 | Better reliability, large-area electrodes directly connected to the substrate, and |
3 | Lower thermal resistance, lower junction temperature, and improved device life |
4 | Better visual consistency, no surface occlusion, excellent viewing angle and |
Sources from Hc Semitek Corporation
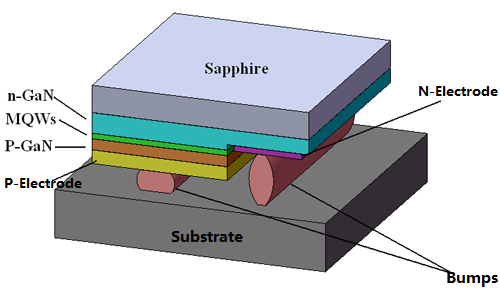
With the development of flip-chip, more LED chips need to be soldered on the panels. Therefore, mass transfer is one of the core technologies in the ultra-fine-pitch mini-LED display industry. The main factors affecting the choices of lead-free solder pastes for LED flip-chips are size and time.
The first aspect is size, which has been mentioned before. The second is die-bonding time. As the pixel pitch shrinks, more LED chips must be mounted on the substrates. Under a fixed chip transfer rate, the required time will be longer, especially for COB flip chips. The chip needs to be placed on a substrate with lead-free solder paste and then process reflow soldering and curing. As the number of chips and the time for chip transfer increase, lead-free solder paste solder products need to stay indoors for a longer time before reflow, which is a challenge to the solder paste performance. The solder paste needs to maintain excellent solderability in an indoor environment for a considerable period after printing, dispensing, jetting, and before reflow soldering. In addition, the lead-free printing solder paste faces the "pause-response" reliability problem. The printing process of lead-free solder paste may be suspended for a while and then start printing again. The characteristics of lead-free solder paste solder should remain unchanged in this case. This is very different from the traditional SMT process.

Fitech's special lead-free solder paste for ultra-fine-pitch die bonding has an excellent performance in long residence time and outstanding "pause-response" performance. In the development stage, the die bonding process is simulated. The product design and production comply with the most stringent standards. At the end of 2021, to deal with the shortcomings of the lead-free solder paste materials in mini-LED and micro-LED packaging, Fitech launched the mLED™ ultra-fine lead-free die bond solder paste series.

Fitech's T7 SAC305 solder paste properties after printing, including viscosity and thixotropy.
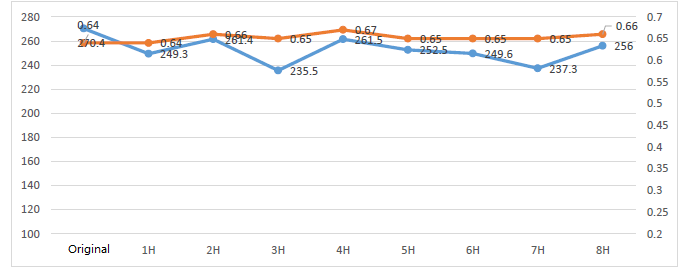
Fitech's T8 SAC305 solder paste properties after printing, including viscosity and thixotropy.
The T7 and T8 mLED™ ultra-fine lead-free die bond solder powders are prepared by the patented technology of liquid-phase-molding spherical alloy powder preparation, which has been optimized by repeated simulation. Fitech provides the most reliable lead-free solder pastes for mini-LED and micro-LED packaging.


















 Back to list
Back to list



