The Failure Modes of Solder Joints (5)
The Failure Modes of Solder Joints (5)
Previous articles have introduced the effects of grain boundary sliding, solder grain growth and orientation, lead contamination, and IMC interfacial voids on solder joints. Voids are one of the direct causes of solder joint failure. The study found that the grain size of the copper pads also influences the reliability of the solder joints, which is reflected in the copper grain size affecting the void growth rate at the pad interface. Voids aggregate to form cracks and lead to solder joints failure. This article will describe the effects of copper pad grain size on solder joints.
Voids are massively distributed at the Cu3Sn/Cu interface and weaken the solder joint mechanical properties, affecting the drop performance, as explained in the previous article. To verify the effects of Cu grain size on the void growth at the Cu3Sn/Cu interface, Li et al. (2015) annealed the ED CCL boards at 150°C for 1000 hours and found that the grain size of the annealed boards increased significantly after reflow. After the aging test, it was observed that the voids of the annealed ED CCL boards were significantly less than unannealed ones, which means that the grain size of the copper pads played a significant role in the void formation. Li et al. believed that although a large number of vacancies still existed after annealing, most of these vacancies could not move freely and could not effectively accumulate into large-area distributed voids. Therefore, maintaining a larger copper grain size has a positive effect on reducing voids.
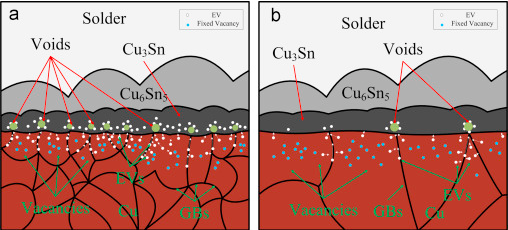
Figure 1: Small Cu grain size (a) is much easily to cause voids than large Cu grain size (b). White Ball: Effective Vacancy (EV); Blue Ball: Fixed Vacancy (Li et al., 2015).
The formation of voids is because of the diffusion rate imbalance of Sn and Cu atoms, which leads to the appearance of vacancies in the IMCs. The copper pad grain size affects the atomic diffusion rate. Smaller grains have more grain boundaries, which provide channels for atom diffusion, creating more vacancies and aggregating to form voids along the grain boundaries.
Reference
Li, H.L., An, R., Wang, C.Q., Tian, Y.H., & Jiang, Z. (2015), “Effect of Cu grain size on the voiding propensity at the interface of SnAgCu/Cu solder joints”, Materials Letters, vol.144, pp.97-99.

















 Back to list
Back to list



